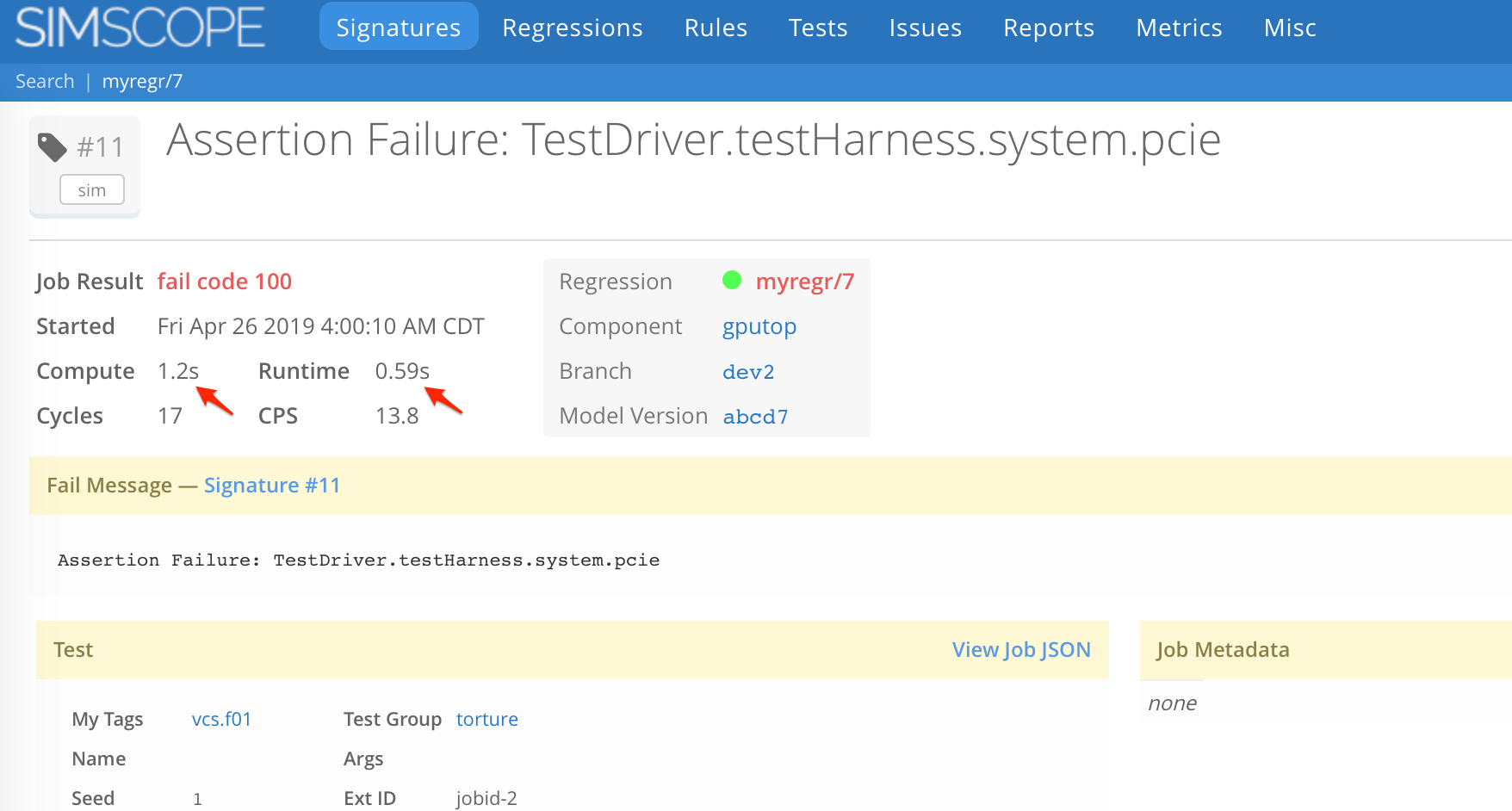
Job Runtime vs Compute Time
Simscope optionally supports separate job runtime and compute time Job fields.
- If runtime and finish_time fields are omitted from the job JSON,
Simscope assumes:
runtime_ms = compute_ms
Purpose of separating Runtime and Compute time
compute_ms— tracks the compute (ie CPU) time of the job. This is used to calculateCPS(cycles-per-second). Sometimes this is called machine time (or machine hours/machine days).runtime_ms— tracks the wallclock duration of the job. This allows separating out non-compute events like license checkout, network/disk load, or pre/post-simulation tasks.
Simscope can chart both job compute time and job runtime fields.
Job time limit
Note: Individual jobs are currently limited to a maximum duration (either runtime or compute)
of 24 days.
- If they exceed this limit, the job will be rejected during import.
Regressions, however, do not have a limit on their duration.
Example Job with separate compute and runtime
This job has separate compute and runtime fields:
Calculating runtime field
start_time and finish_time
If your job JSON has both start_time and finish_time fields,
runtime is automatically inferred as:
# Job runtime (milliseconds)
job.runtime_ms = (job.finish_time - job.start_time) * 1000
This example JSON infers a runtime_ms of 9080000 milliseconds (ie 15 min, 8 sec) and
a compute_ms of 780200 milliseconds (ie 13 min):
{
"start_time": "2021-05-07T02:00:10-05:00",
"finish_time": "2021-05-07T02:15:18-05:00",
"compute_ms": 780200
...
}
Explicit compute_ms field
If you want to specify job runtime and compute explicitly (in milliseconds), your JSON
should have start_time, compute_ms, and runtime_ms fields.
This example has a compute time of 45.238 seconds and a runtime of 47.5 seconds:
{
"start_time": "2021-05-07T02:00:10.000111-05:00",
"compute_ms": 45238,
"runtime_ms": 47500
...
}
CPS calculation
CPS (cycles per second) is a simple metric to track simulation performance.
- Over time, if this reduces, you are using extra (ie wasting) compute to run the same number of simulation cycles.
- CPS can be charted, to track it's value over time.
CPS is calculated within Simscope as:
cps = total_cycles / (total_compute_ms / 1000)
Notes:
- Simscope uses the
compute_msvalue (job CPU time), notruntime_ms(job wallclock runtime) for CPS calculation. - Simscope ignores any jobs where
cycles = 0.- This prevents non-simulations (e.g.
lint,compile, etc) from affecting CPS.
- This prevents non-simulations (e.g.
CPS Pass-only vs Pass+Fail
Simscope calculates CPS using two different methods:
- CPS Pass-only — cycles-per-second among pass jobs only.
- This is the recommended use for tracking long term performance, as it is a more stable value, unaffected by early failing simulations, which usually.
- CPS Pass+fail — cycles-per-second among all matching jobs.